$150.00
Description
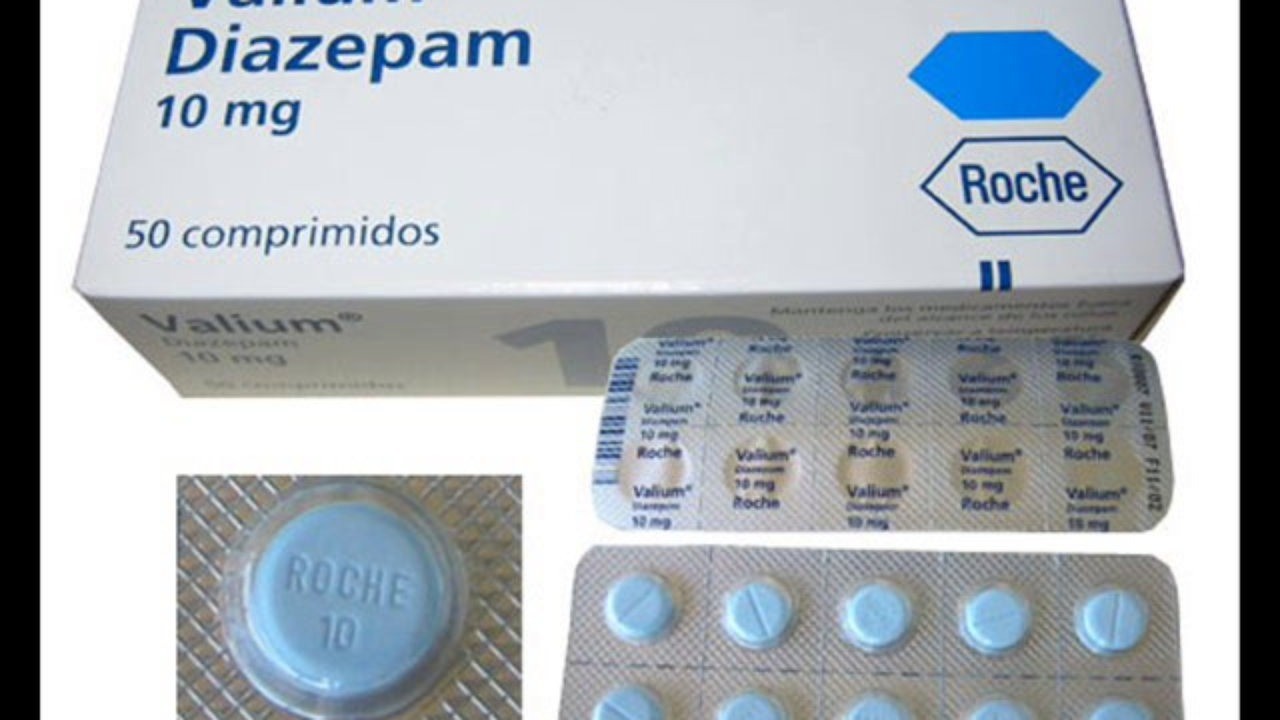
Diazepam
Brand Names: Valium
Generic Name: Diazepam
Manufacturer: Richter
How does Valium work?
Diazepam is a type of medicine called a benzodiazepine. Benzodiazepines are used for their sedative and anxiety-relieving effects.
Diazepam works by acting on receptors in the brain called GABA receptors. This causes the release of a neurotransmitter called GABA in the brain.
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are stored in nerve cells in the brain and nervous system. They are involved in transmitting messages between the nerve cells. GABA is a neurotransmitter that acts as a natural ‘nerve-calming’ agent. It helps keep the nerve activity in the brain in balance, and is involved in inducing sleepiness, reducing anxiety and relaxing muscles.
As diazepam increases the activity of GABA in the brain, it increases its calming effect and results in sleepiness, a decrease in anxiety and relaxation of muscles.
Diazepam has several uses. Firstly, it can be used to calm severe anxiety and agitation. For example, benzodiazepines such as diazepam are effective at quickly reducing the symptoms of anxiety and agitation that occur in a manic episode of the psychiatric illness, bipolar affective disorder. A benzodiazepine may be given as part of the initial treatment of a manic episode, though they are not licensed specifically for this purpose. Benzodiazepines help calm the individual while the main medicines for this condition (mood stabilisers) begin to take effect.
Oral forms of diazepam are also used for short-term treatment of severe anxiety associated with insomnia, as well as for night terrors and sleep-walking in children. Diazepam decreases the time taken to fall asleep and nocturnal awakenings, as well as increasing the total amount of time spent sleeping. However, it is only suitable for short-term treatment of insomnia and anxiety as it has a high potential for dependence and addiction. As diazepam remains active in the body for many hours, drowsiness may also persist into the next day.
Diazepam is also given for its sedating and anxiety-relieving effects as a pre-med before surgery or medical investigations or procedures, and to alcoholics during acute alcohol withdrawal.
The second main use of diazepam is in controlling convulsions, for example epilepsy, or seizures associated with fever in children (febrile convulsions). It is particularly useful for controlling repeated epileptic fits when a patient does not recover conciousness between fits (status epilepticus). Diazepam helps control convulsions because the increased activity of GABA that it causes in the brain helps to calm excessive electrical nerve activity that is responsible for causing seizures.
A further use of diazepam is in controlling muscle spasms due to tetanus or poisoning.
Diazepam may be given as tablets, oral solution, injection or a rectal solution, depending on what condition is being treated.
What is it used for?
• Short-term treatment of severe anxiety or agitation
• Short-term treatment of severe insomnia (oral forms only)
• Night terrors and sleepwalking in children (oral forms of only)
• Acute alcohol withdrawal (used in combination with other treatment)
• Convulsions, eg epilepsy
• Repeated fitting with no recovery of consciousness between seizures (status epilepticus)
• Fitting associated with fever (febrile convulsions)
• Muscle spasms due to tetanus or poisoning
• Relieving anxiety and causing sedation prior to surgery or medical procedures (pre-med)
Warning!
• This medicine is generally only suitable for short-term use. If it is used for long periods or in high doses, tolerance to and dependence upon the medicine may develop, and withdrawal symptoms may occur if treatment is stopped suddenly. For this reason, treatment with this medicine should usually be stopped gradually, following the instructions given by your doctor, in order to avoid withdrawal symptoms such as rebound insomnia or anxiety, confusion, sweating, tremor, loss of appetite, irritability or convulsions.
Additional information
| Type | 0.5mg, 1mg, 2mg, 4mg, 5mg, 6mg, 8mg, 10mg, 12mg, 15mg, 20mg, 25mg, 30mg, 40mg, 50mg, 100mg, 200mg, 250mg, 275mg, 325mg, 500mg, 50amps, 1 Vial, 3 Vials, 6 Vials, 1 Ampoule, 3 Ampoules, 5 Ampoules, 50 Ampules, 100 Ampules, 2000 I.U, 5000 IU, 10000 IU |
|---|---|
| Units | 1 Unit, 3 Units, 5 Units, 7 Units, 10 Units, 1 Pill, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 100 pills, 120 pills, 150 pills, 200 pills, 240 pills, 200 tabs, 300 tabs, 600 tabs, 1,000 tabs |